PARMS Retic
PARMS Retic is an integrated suite of computer-based models developed in conjunction with the Australian water sector to help manage the renewals of water supply reticulation pipes.
The PARMS software allows management strategies to be analysed over the strategic planning horizon to understand long term budget needs, the level of renewal needed to meet strategic goals, and the implications of increasing or decreasing expenditure.
By virtue of its design philosophy and robust framing, PARMS underpins asset management aligned with ISO 55000.
The software is tailored for use by individual utilities through the development of bespoke deterioration curves based on analysis of the utility’s asset and failure data. Cost models and settings are also defined based on utility-specific data.
While consideration of failure consequences is more associated with critical (T&D) assets, PARMS Retic provides the facility to integrate a broad range of consequence and other risk factors to help in the prioritisation of capital spent. Consequences such as traffic disruption and customer impacts are also an integral part of the strategic simulation.
PARMS has been used by utilities across Australia to analyse their rehabilitation strategies and then cost-effectively target renewals. It is accepted by regulators as representing good practice and has been shown to provide significant financial and economic benefits in comparison to legacy approaches. For example, one study found that a utility could have achieved the same asset management outcomes at 60% of the cost by using PARMS, representing a saving of tens of millions of dollars over a five-year period.
The strategic modelling allows the impact of a range of management levers to be analysed:
| Policy Focus | Detail |
|---|---|
| Changing renewal triggers |
|
| Making additional & preferential replacements |
|
| Setting budget constraints Other network management options |
|
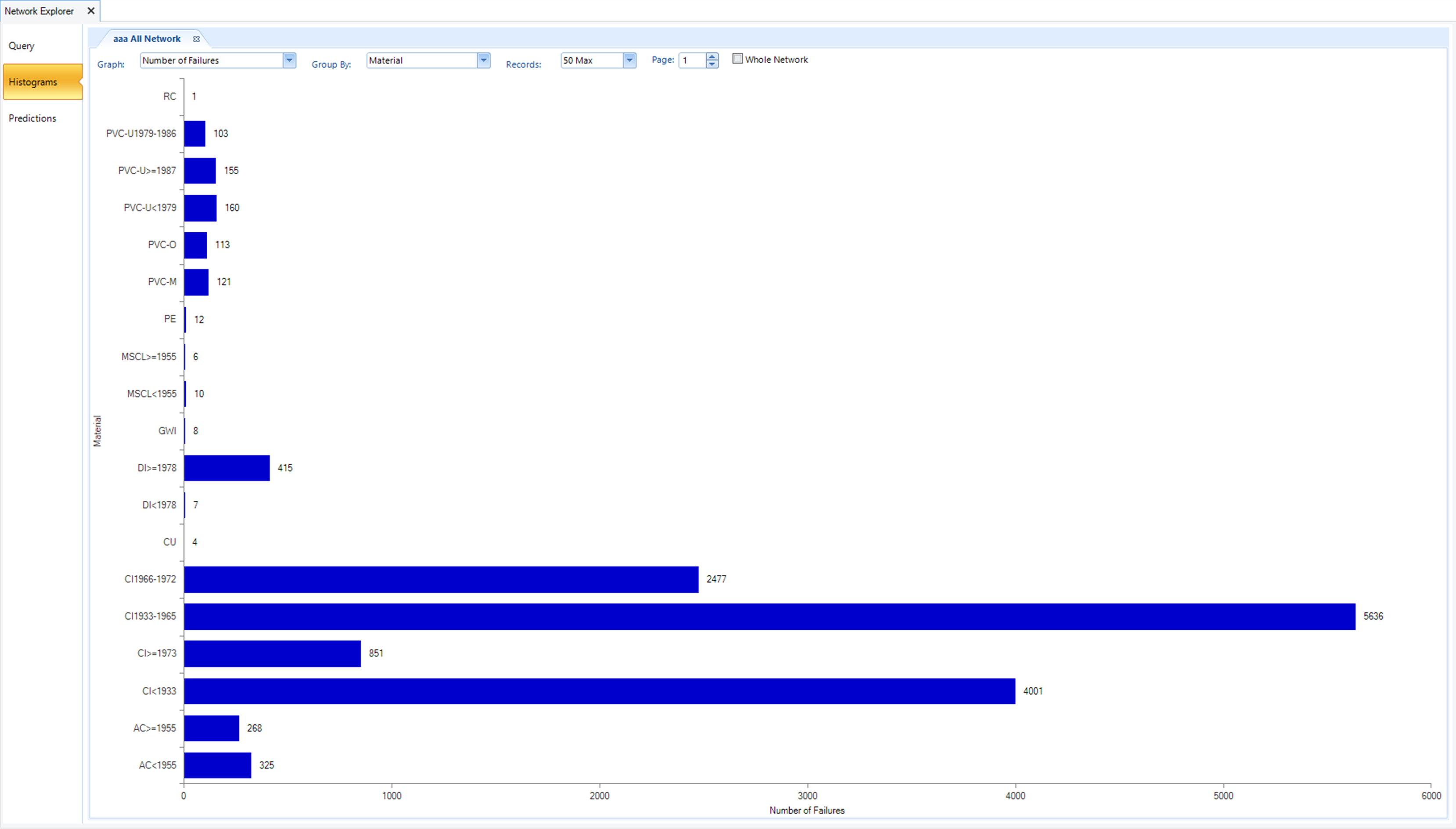
Data Exploration and Visualisation
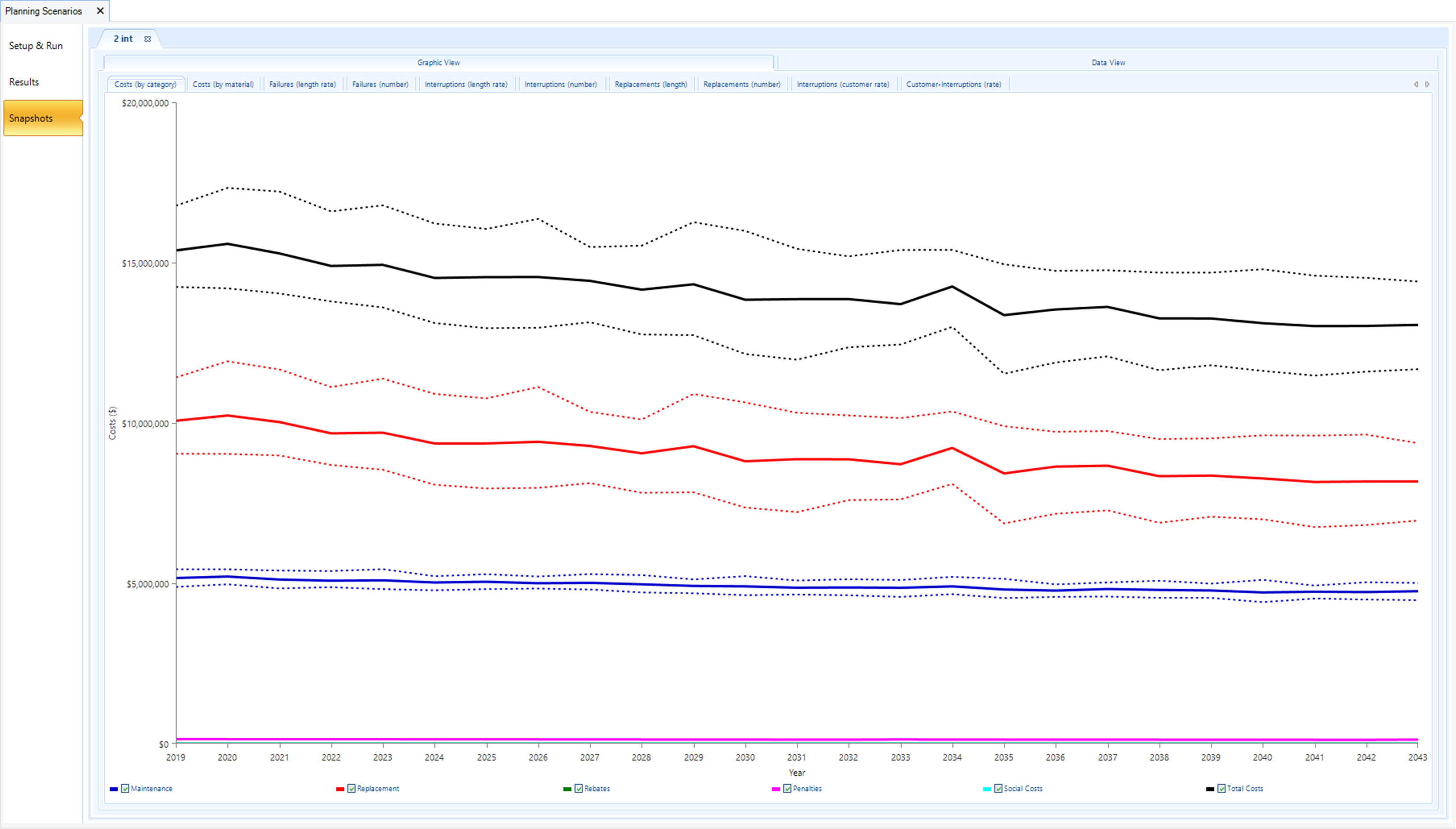
Modelling of Cost (Totex) Streams
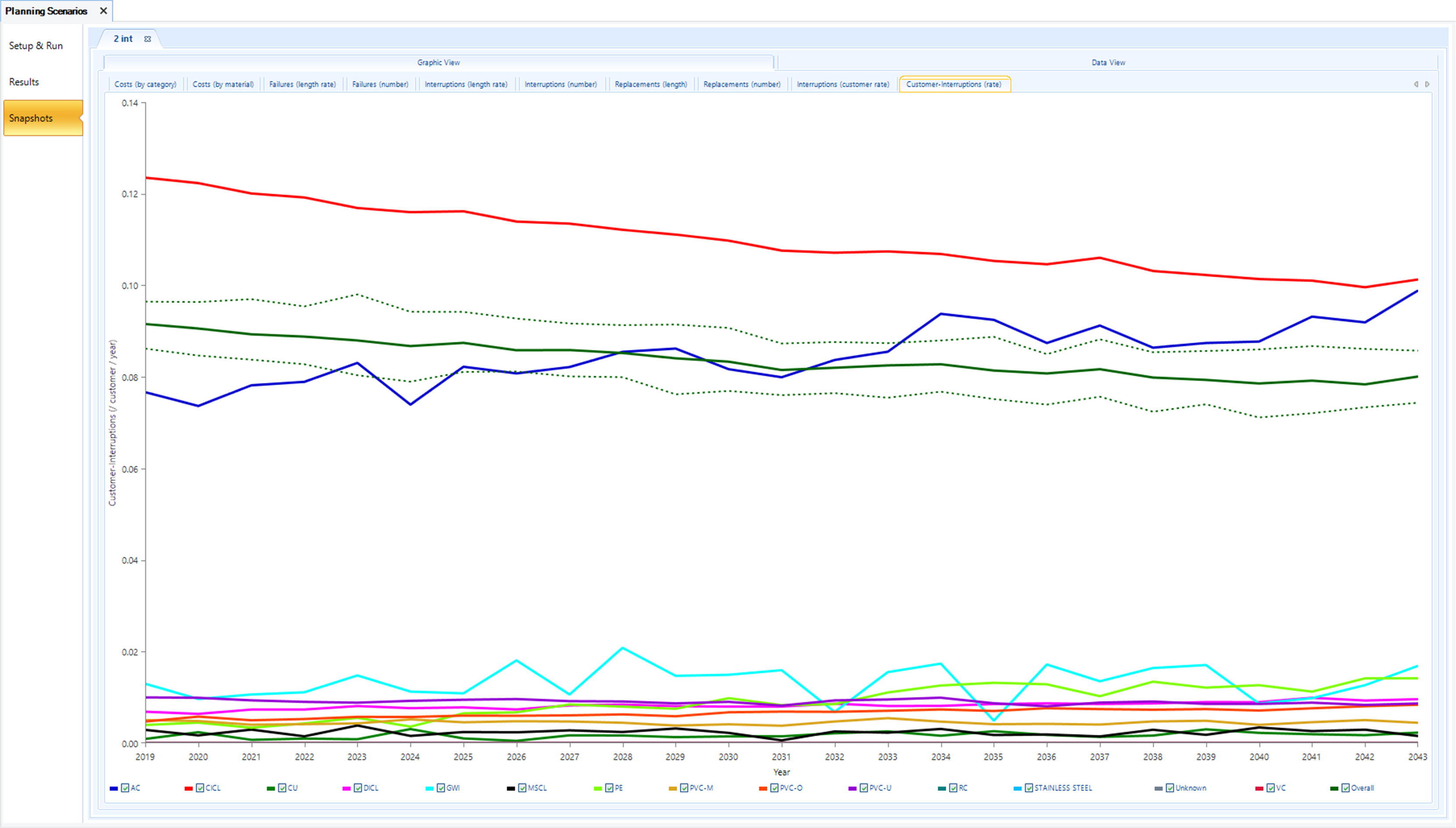
Impacts on Customer Service Levels (Customer-Interruptions/Customer)